Pump for use in low-lift pumping stations
Pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are tubular casing pumps and are deployed, as the name suggests, in pumping stations of the low lift type. These are used for land drainage or irrigation. See Fig. 1 Pump for use in low-lift pumping stations
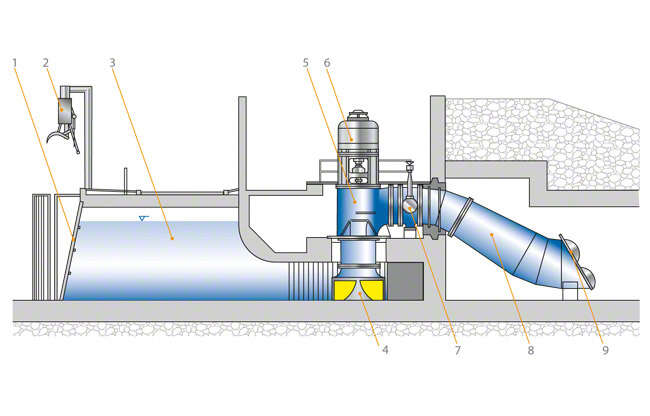
Fig. 1 Pump for use in low-lift pumping station: Low-lift pumping station 1 Trash screen; 2 Screen cleaning machine; 3 Intake chamber; 4 Inlet cone; 5 Pump; 6 Drive; 7 Butterfly valve; 8 Discharge line; 9 Circular flap valve (with hollow float flap)
Coastal areas lying below the high water mark and enclosed by dykes need to be regularly drained. As a general rule, several smaller pumping stations spread over a catchment area feed into a large main pumping station.
If the gravity drainage flow through the dyke's tide gate or sluice ceases because of a high external water level, the pump for use in low-lift pumping station is started up.
In regions affected by water shortage, irrigation is needed (see Irrigation pump). Frequently, a main pumping station situated on the banks of a river or lake supplies several smaller intermediate stations via a system of ditches, where the pump installed pumps the water to the fields located at higher level. In a few cases, a low-lift pumping station serves both applications, with the land being either drained or irrigated depending on the season.
Because of the low heads involved, propeller pumps with axialpropellers are typically the design of choice. Most pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are installed vertically, with a popular configuration being a submersible motor pump installed in a discharge tube. See Fig. 2 Pump for use in low-lift pumping stations
If the gravity drainage flow through the dyke's tide gate or sluice ceases because of a high external water level, the pump for use in low-lift pumping station is started up.
In regions affected by water shortage, irrigation is needed (see Irrigation pump). Frequently, a main pumping station situated on the banks of a river or lake supplies several smaller intermediate stations via a system of ditches, where the pump installed pumps the water to the fields located at higher level. In a few cases, a low-lift pumping station serves both applications, with the land being either drained or irrigated depending on the season.
Because of the low heads involved, propeller pumps with axialpropellers are typically the design of choice. Most pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are installed vertically, with a popular configuration being a submersible motor pump installed in a discharge tube. See Fig. 2 Pump for use in low-lift pumping stations
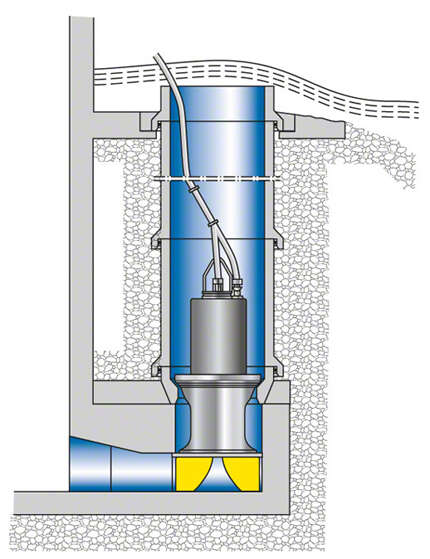
Fig. 2 Pump for use in low-lift pumping station: Submersible motor propeller pump installed in discharge tube for use in low-lift pumping station
In the past, propeller pumps installed at an inclination were in wide-spread use for large flow rates. Nowadays there is a preference for vertical pumps with pull-out rotating assemblies (see Pump in pull-out design).
Pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are typically driven by an electric motor either directly or via a gear unit. In remote areas, a Diesel engine is frequently used.
Adaptation to changing flow rates and changing heads, caused for example by high water or changing tides, is facilitated by a Diesel engine with speed control (see Closed-loop control).
Large pump sets driven by electric motors are often equipped with variable pitch propellers (see Impeller blade pitch adjustment)sometimes combined with speed control by pole-changing motors or by changing the frequency.
The data of typical pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are: flow rates (Q) of 500 to 60,000 m³/h (and more), heads (H) of 0.5 to 8 m and nominal diameters (DN) of the discharge nozzle of 300 to 2400 mm (and larger).
Adaptation to changing flow rates and changing heads, caused for example by high water or changing tides, is facilitated by a Diesel engine with speed control (see Closed-loop control).
Large pump sets driven by electric motors are often equipped with variable pitch propellers (see Impeller blade pitch adjustment)sometimes combined with speed control by pole-changing motors or by changing the frequency.
The data of typical pumps for use in low-lift pumping stations are: flow rates (Q) of 500 to 60,000 m³/h (and more), heads (H) of 0.5 to 8 m and nominal diameters (DN) of the discharge nozzle of 300 to 2400 mm (and larger).
