Irrigation pump
Irrigation pumps are used to pump water from a lower to a higher level from which the water then flows through channels to the fields requiring irrigation (lift operation) or to raise it to the required pressure head so that it can be sprayed on the fields via piping systems (sprinkling). The heads involved range from approx. 1 m for normal lift operation to 40 m for sprinkling. In special cases, heads exceeding 100 m may be required.
The flow rate varies according to the area to be irrigated, the nature of the soil, the type of crop cultivated and the climate. A quantity of 1 to 2 litres per second and hectare can be assumed as a rough value for orientation.
Suitable pump types for heads up to 10 m
- Tubular casing pumps with axial propeller
See Fig. 1 Pump casing - Tubular casing pumps with submersible motors
See Fig. 1 Irrigation pump
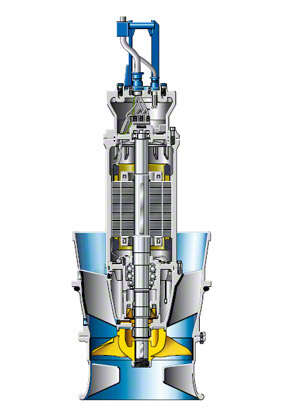
Fig. 1 Irrigation pump: Maintenance-free propeller pump with submersible motor and adjustable blades (cf. Fig. 2 Pump for use in low-lift pumping station)
Suitable pump types for heads above 10 m
- Tubular casing pumps with mixed flow impellers
See Fig. 2 Irrigation pump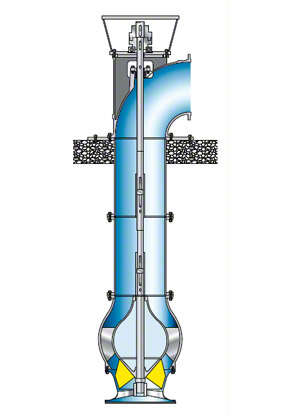
Fig. 2 Irrigation pump: Tubular casing pump with mixed flow impeller
- Submersible motor pumps with mixed flow impellers
See Fig. 5 Cooling water pump - Single- or double-entry volute casing pumps with mixed flow impellers
Irrigation pumps are usually not equipped with variable speed drives. The flow rate can however be controlled either by switching the pumps on and off, or by using a throttling valve in the discharge pipe, pre-swirl control (e.g. cooling water pumps), rotational speed or impeller blade pitch adjustment. Both horizontal and vertical pumps (e.g. tubular casing pump) are used as irrigation pumps.
