Standard orifice
The standard orifice is also referred to as a measuring orifice or simply an orifice and is a differential pressure measuring instrument. It comprises an orifice plate that is inserted into piping and has a bore hole diverging in the flow direction to measure the flow rate. When a fluid passes through the orifice, a differential pressure is produced (see BERNOULLI) between the measuring points "upstream of the orifice" (positive pressure) and in the "narrowest cross-section" (negative pressure) so that the flow rate can be calculated. See Fig.1 Standard orifice
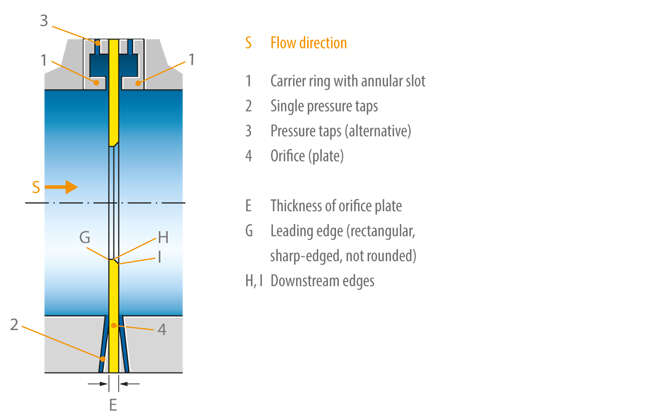
Fig. 1 Standard orifice: General design
The term "measuring orifice" is used to make a distinction to an orifice that is used to throttle (see Closed-loop control) the flow rate. With respect to its geometric dimensions, surface quality, and installation conditions (e.g. minimum lengths of straight pipe runs upstream and downstream of orifice), the standard orifice meets the requirements defined by a standard (e.g. DIN EN ISO 5167) that also provides detailed information about measurement accuracy and application limits.
The flow volume is calculated based on the differential pressure level measured and the formula for differential pressure measuring instruments. The flow coefficient (C) is depicted in a table in Appendix A of DIN EN ISO 5167-2:2022-6 (also see Standard nozzle, Standard Venturi nozzle, Venturi tube).
