Frequency inverter
A frequency inverter is an electronic device that receives three-phase or alternating current and changes the output voltage in amplitude and frequency. This is then used to improve the run-up and speed behaviour of three-phase motors (also see Starting method). Frequency inverters also control the rotational speed of single-phase asynchronous motors, whereby the inverter energises the second phase previously generated by the capacitor.
Core components of the frequency inverter include a rectifier that feeds a direct-current or direct-voltage link and an inverter powered by this link. The inverter generates a voltage whose mean waveshape corresponds to the sinusoidal voltage of the required frequency and amplitude. See Fig. 1 Frequency inverter
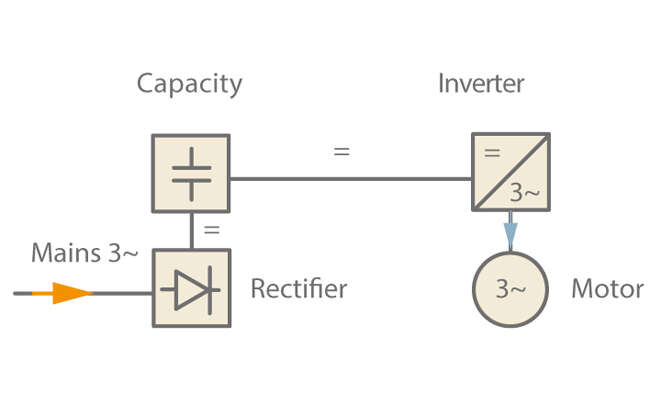
Fig. 1 Frequency inverter: Simplified schematic
Three-phase motors operated using a frequency inverter can infinitely vary their rotational speeds from zero up to their nominal speed without experiencing a drop in torque. Since frequency inverters produce substantial electrical interference along the motor supply cable, they must frequently be shielded (see Shielding). A sine filter between the frequency inverter and the motor can also suppress interference.